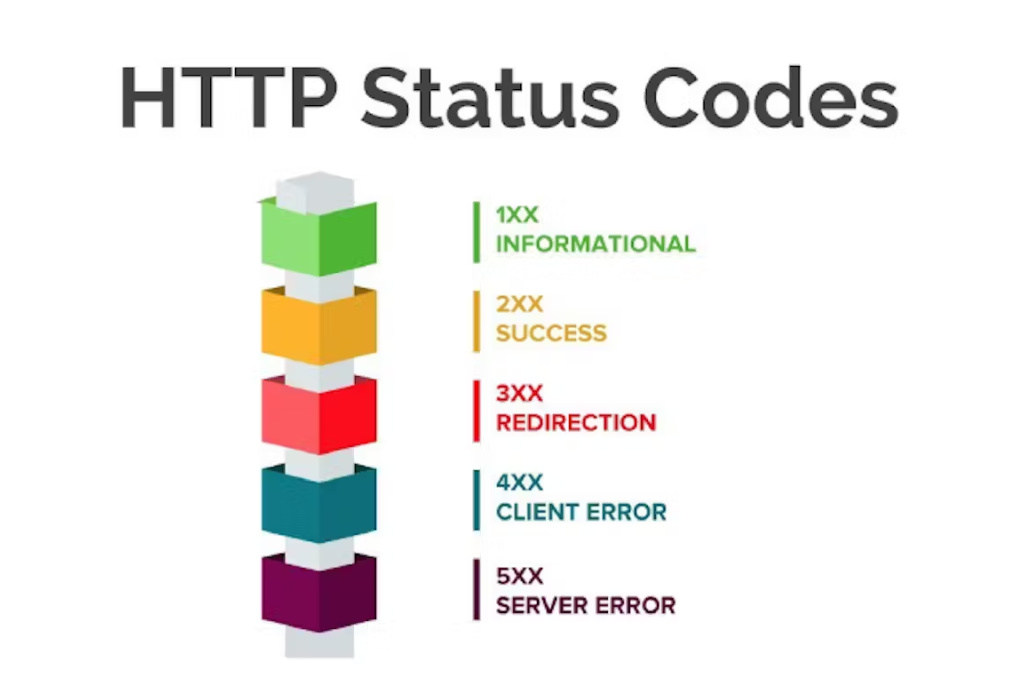
✅ HTTP Status Codes Overview
HTTP status codes are grouped by their first digit:
| Range | Type | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| 1xx | Informational | Ongoing communication |
| 2xx | Success | Everything is OK |
| 3xx | Redirection | Further action needed |
| 4xx | Client Error | ⚠️ Your (client’s) fault |
| 5xx | Server Error | 💥 Server's fault |
✅ 2xx — Success Responses
These mean:
✅ “Everything worked!” — the server understood and processed your request successfully.
| Code | Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | OK | Standard response for a successful request. Everything is fine. |
| 201 | Created | A new resource was successfully created (e.g., after a POST). |
| 202 | Accepted | Request accepted for processing, but not completed yet (e.g., queued). |
| 203 | Non-Authoritative Info | Server returned info from a third party (e.g., proxy), not original source. |
| 204 | No Content | Success, but nothing to return in the body. Often used in DELETEs. |
| 205 | Reset Content | Tells client to reset the form/view. Rare. |
| 206 | Partial Content | Partial response (e.g., used for range requests — like video streaming). |
🧠 These are your happy codes — everything worked, and your app can proceed.
🔁 3xx — Redirection Responses
These mean:
📍 “You’re in the right direction, but need to go somewhere else to complete it.”
| Code | Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 300 | Multiple Choices | Several options for the resource (e.g., language versions). |
| 301 | Moved Permanently | Resource moved forever to a new URL. Update bookmarks. |
| 302 | Found (Temp Redirect) | Temporarily moved. Come back to the original URL next time. |
| 303 | See Other | Redirect to another URI using a GET request. Common after POSTs. |
| 304 | Not Modified | Resource not changed since last request. Use your cache. |
| 305 | Use Proxy (Deprecated) | Use a proxy to access this resource. Almost always ignored today. |
| 306 | (Unused) | Reserved but not used anymore. |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect | Like 302, but preserves method (e.g., POST stays POST). |
| 308 | Permanent Redirect | Like 301, but preserves method. |
🧭 These codes tell the browser or client where to go next — either temporarily or permanently.
🔴 4xx — Client Error Responses
These mean you (the client) did something wrong. Examples:
| Code | Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request | Your request is malformed (e.g., bad JSON, missing parameters). |
| 401 | Unauthorized | You need to authenticate (e.g., missing/invalid token). |
| 403 | Forbidden | You're authenticated but not allowed to access the resource. |
| 404 | Not Found | The requested resource doesn’t exist. |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed | You used the wrong HTTP method (e.g., POST instead of GET). |
| 422 | Unprocessable Entity | Semantically correct but invalid data (common in APIs). |
| 429 | Too Many Requests | You're being rate-limited (too many requests in a short time). |
🧠 These errors usually mean you need to fix the request — your app, form, or client made a mistake.
🔥 5xx — Server Error Responses
These mean the server failed while trying to process a valid request.
| Code | Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | Internal Server Error | A generic error — the server crashed or had an unexpected issue. |
| 501 | Not Implemented | Server doesn't support the request method or functionality. |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | A proxy/gateway received an invalid response from upstream. |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | Server is down or overloaded. Retry later. |
| 504 | Gateway Timeout | Timeout from upstream server — the backend took too long. |
⚠️ These errors are not your fault as the client — the server or its configuration needs to be fixed.
🔍 Summary: Who Needs to Act?
| Code Type | Meaning | Who Acts? |
|---|---|---|
| 2xx | ✅ Success | You (client) can proceed |
| 3xx | 🔁 Redirection | Browser/client must follow |
| 4xx | ❌ Client Error | You (client) must fix request |
| 5xx | 💥 Server Error | Server must fix the issue |
✅ Real-World Developer Tips
-
: ✅ Most common for GETs, success in general. -
: 🔧 Used after creating something via POST. -
: 🗑️ Used when deleting or toggling status — no need for body. -
: 🔁 Good for SEO — permanent redirects. -
: 🔁 Good for temporary testing or login flows. -
: ⚡ Improves performance by using cache.