If you’ve ever wondered why your callback runs after your , or what makes so special,here’s my take on how the event loop really works, minus the textbook jargon.
🧠 Node.js Event Loop: The Real-World Version
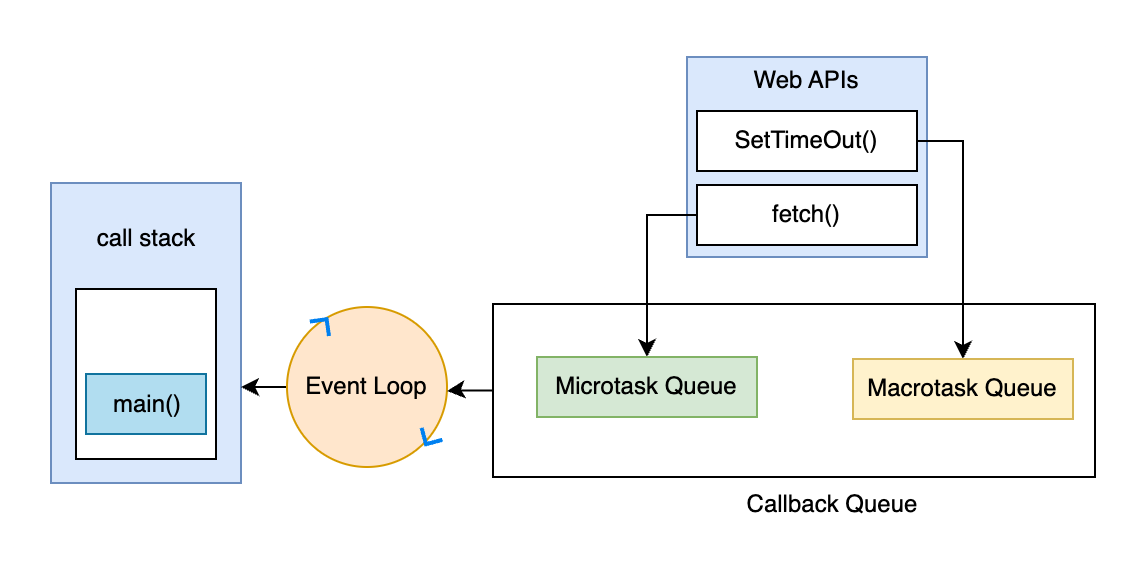
Node.js runs everything on a single thread, but it’s surprisingly good at juggling lots of things at once. The secret? It splits up work into macrotasks and microtasks—think of them as two different to-do lists.
Each time Node.js goes through its event loop (a “tick”), it:
- Runs one macrotask.
- Then, empties the microtask queue (runs all microtasks).
- Then, moves on to the next macrotask.
🟩 Macrotasks: The Big Stuff
Macrotasks are the “main events”—timers, I/O, and things you schedule with:
- setTimeout()
- setInterval()
- setImmediate() (Node.js only)
- I/O callbacks (like reading files or handling HTTP requests)
Example:
setTimeout(() => {console.log('Macrotask: Timeout');}, 0);
Macrotasks always wait for microtasks to finish before they run.
🟦 Microtasks: The Quick Fixes
Microtasks are the “urgent” tasks—stuff that should happen right after the current code finishes, but before any new macrotask starts.
You get microtasks from:
- Promise.then() / catch() / finally()
- queueMicrotask()
- process.nextTick() (special Node.js case—see below!)
Example:
Promise.resolve().then(() => {console.log('Microtask: Promise.then');});
🔁
is Node’s way of saying, “Run this callback before anything else, even before other microtasks.”
Example:
process.nextTick(() => {console.log('process.nextTick');});
⚠️ Heads up: If you keep scheduling inside itself, you can starve the event loop—nothing else will get a turn.
🕘 Who Runs First? (Execution Order)
Let’s see it in action:
console.log('Start');setTimeout(() => {console.log('Macrotask: setTimeout');}, 0);Promise.resolve().then(() => {console.log('Microtask: Promise.then');});process.nextTick(() => {console.log('Microtask: process.nextTick');});console.log('End');
What you’ll see:
StartEndMicrotask: process.nextTickMicrotask: Promise.thenMacrotask: setTimeout
🧭 Quick Reference Table
| Task Type | How You Get One | When It Runs |
|---|---|---|
| Macrotask | setTimeout, setInterval, I/O | After all microtasks |
| Microtask | Promise.then, queueMicrotask | Before macrotasks, after current code |
| process.nextTick | process.nextTick() | Before all other microtasks |